Introduction to Brain Waves
There are five different types of brain waves that function in a manner similar to musical notes. Some have a low frequency of action, whereas others have a greater frequency of action. However, when they work together, they may create a harmonious song in which our thoughts, emotions, and sensations can find a perfect balance, and in which we can feel more focused and sensitive to everything that surrounds us.
Furthermore, there has recently been discussion of biofeedback equipment, which are capable of triggering specific waves in our brains, allowing us to achieve specific states of consciousness as a result of using them. The reality is that it is prudent to use caution while dealing with this information. It is important that each of our brain waves functions properly, within its frequency range, and at an optimal level in order to achieve actual well-being. Furthermore, we cannot disregard the fact that these brain rhythms are not constant, but rather fluctuate as we grow, mature into our senior years.

The goal is not to get concerned with increasing Beta waves in order to better attention or Gamma waves in order to achieve some sort of mystical or spiritual condition, as some people believe. The reality is that there is no form of brain wave that is superior to another or that is more unique when compared to the others. They are all significant since they are all the outcome of the electrical activity of our neurons as well as the frame of mind in which we are currently experiencing them.
The various forms of brain waves that exist
In fact, neurologists have stated that if all of our nerve cells were stimulated at the same time, we would be able to generate enough energy to light a single light bulb. The information is, without a question, astounding. Thus, the different types of brain waves are produced by all of this electrical activity. Everything we do and think may generate a certain form of brain wave, and this process is both intricate and intriguing. It is a kind of flawless process.
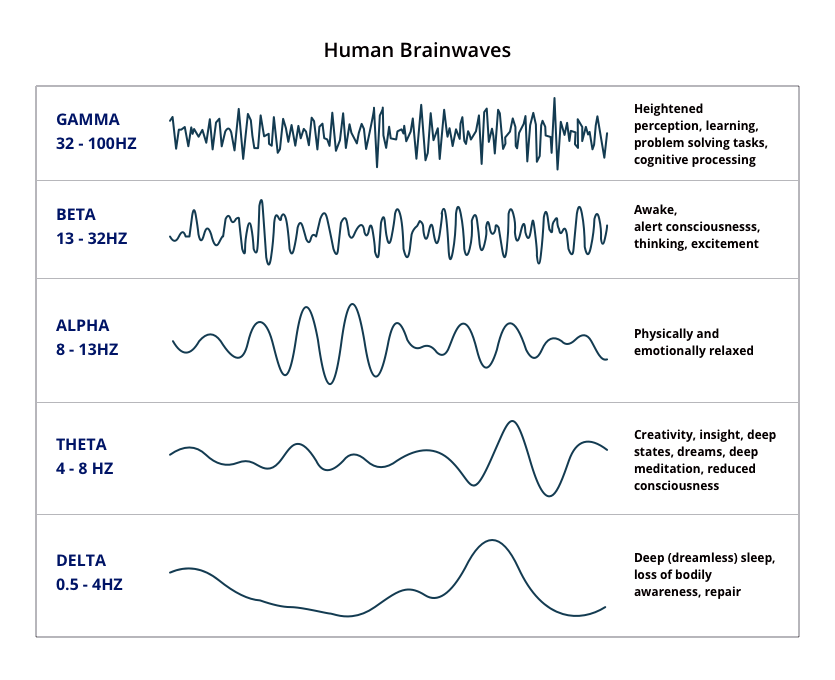
On the other hand, it is critical to emphasize that our brain maintains the activity of the five types of brain waves over the course of the day. Depending on what we do at each moment, some waves will show greater activity in certain areas of our brain, and others will work with less intensity in other areas, but none of them will be, so to speak, “disconnected”. There are certain very special details that need to be taken into consideration in this situation. See below for a description of the many types of brain waves and how their effects are classified and measured.
-
Delta Waves (1 to 3 Hz)

These are the waves with the largest wave amplitudes, and they are associated with profound sleep and dreaming (but without dreams). The fact that they are so abundant in newborns and young children is particularly interesting to note because this form of wave is becoming less and less common as we grow older. The fact is that sleep and our ability to relax are gradually eroded over time as we get older.
This sort of wave is, on the other hand, mostly associated with body functions that we are not aware of, such as heart rate control and digestion.
-
Theta waves (3.5 to 8 Hz)
The second kind of brain wave has a frequency range of 3.5 to 8 Hz and is mostly associated with our inventive abilities, as well as with contemplation and sleep. As a matter of interest, it should be noted that theta waves are known to be highly active while we are experiencing really intense emotions.
When we complete an effort or complete a work that has required a significant amount of energy, we might be aware that this sort of wave has taken control of the situation. Theta waves become more prominent in our brains at precisely the moment when we relax and allow our imagination to “fly”.
-
Alpha waves (8 to 13 Hz)

During that period of transition between sleep and wakefulness, when there is a sense of peace but not slumber when there is relaxation and a condition suitable to meditation, the Alphas emerge. We can even feel it when we are sitting on the couch watching television or lying in bed relaxing, but we are not sleeping.
A high level of alpha waves might make it difficult for us to concentrate on a task or perhaps feel as if we had very little strength to do it. Anxiety, tension, and sleeplessness are all caused by a low level.
-
Beta waves (12 to 33 Hz)

We have already crossed the threshold of those sorts of brain waves, whether at a low or moderate level and are on our way to taking the next step. We have already entered the range of higher frequencies that are produced as a result of high levels of neural activation.
All that has to be mentioned is that we are dealing with incredibly intriguing states that are also quite complicated. States that are associated with those daily tasks in which we devote all of our attention, in which we must be vigilant and be aware of a variety of stimuli, are called alert states.
Activities as routine as driving, passing an exam, giving a presentation, participating in a work meeting when a project is presented, and so on, are times when the brain is most active. However, an excess of neural activity, or neuronal over-activation, can result in a condition of worry or stress that can be harmful to humans.
The results of research in this field are still being discovered. Recently released research by a team of neuroscientists from the famous Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) discovered a significant discovery concerning beta waves that were previously unknown.
-
Gamma waves (25 to 100 Hz)

We all know that when we hear the word “gamma,” we instantly think of the well-known gamma rays, which are known for their long wavelengths and strong levels of electromagnetic radiation. Gamma waves and gamma rays, on the other hand, are only similar in one respect: they both have an extraordinarily rapid frequency.
What role does music have in our brain’s interpretation?
It was created by the University of Florida to demonstrate how our brain processes music and the advantages it may have on our life.
Music is created by the vibrations produced by an instrument, by the voice, or by some other source of vibration. These waves are transported through the air by means of which the outer ear picks up the sound and directs it to the place where the eardrum is located before passing to the middle ear.
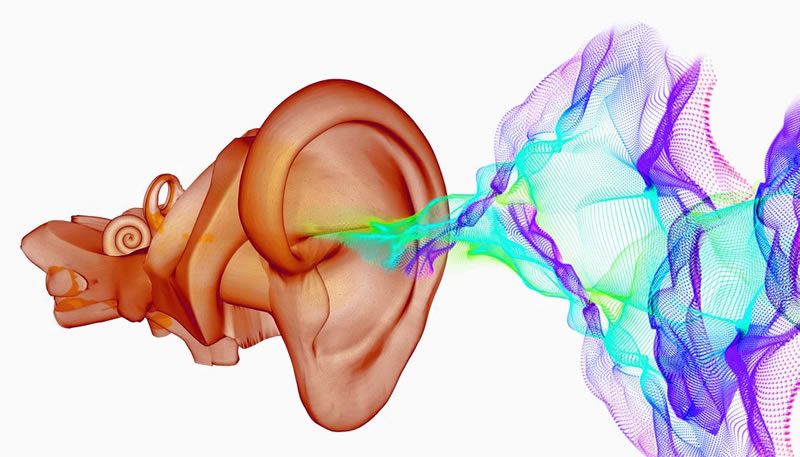
Once within the ear, the sound waves are amplified by three microscopic bones located in the center of it before they can reach the inner ear. Last but not least, these waves are turned into electrical impulses, which are then transferred to the brain via the auditory nerves, and it is at this point that the brain begins to interpret them in terms of “sound.”
Check the playlist “Binaural Beats – Brain Waves” on our Youtube channel “Beautiful Relaxing Music”:
